
How Does Copper Clad Plate Perform in High-Temperature Applications?
2025-01-07 09:04:41
How Does Copper Clad Plate Perform in High-Temperature Applications?
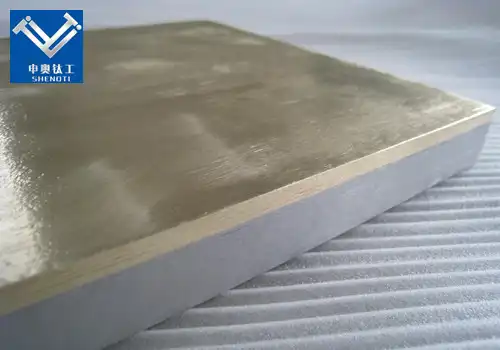
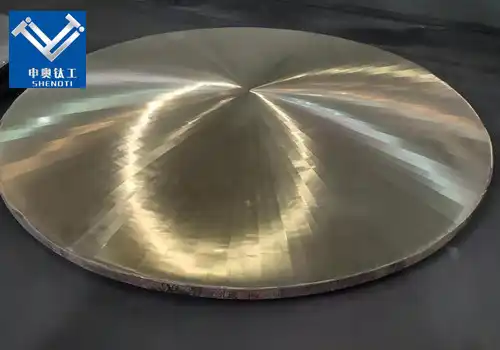
Copper clad plates (CCPs) are composite materials that combine the advantageous properties of copper with those of a substrate material, such as steel or aluminum. This combination results in a material that offers excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. These attributes make CCPs particularly suitable for high-temperature applications across various industries.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper Clad Plates in High-Temperature Environments?
In high-temperature settings, materials must maintain their structural integrity and performance. CCPs exhibit several key properties that make them suitable for such conditions:
Thermal Conductivity: Copper's high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial in applications like heat exchangers and power electronics. This property helps in maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating.
Mechanical Strength: The substrate material, often steel or aluminum, provides mechanical strength and durability. This combination allows CCPs to withstand thermal stresses and mechanical loads without deforming or failing.
Corrosion Resistance: The copper layer offers excellent corrosion resistance, protecting the underlying substrate from oxidative damage, which is especially important in high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Thermal Stability: CCPs maintain their properties over a wide temperature range, ensuring consistent performance even under fluctuating thermal conditions.
How Are Copper Clad Plates Manufactured to Withstand High Temperatures?
The manufacturing process of CCPs is critical in determining their performance in high-temperature applications. Common methods include:
Explosive Welding: This technique uses controlled explosive energy to bond copper and the substrate material at the atomic level, creating a metallurgical bond that can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Roll Bonding: In this process, copper and the substrate are passed through rollers under high pressure, resulting in a strong bond. The bonded materials are then heat-treated to enhance their mechanical properties.
Direct Bonded Copper (DBC): This method involves bonding copper directly onto a ceramic substrate, such as alumina or aluminum nitride, at high temperatures. DBC substrates are commonly used in power electronics due to their excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
Each of these methods ensures that the resulting CCPs have a uniform and defect-free bond, which is essential for maintaining performance in high-temperature environments.
What Are the Common Applications of Copper Clad Plates in High-Temperature Settings?
CCPs are utilized in various high-temperature applications across multiple industries:
Power Generation: In power plants, especially in condenser tubes and heat exchangers, CCPs maximize heat transfer efficiency. Copper's excellent thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat exchange, while the substrate provides structural integrity, making these plates ideal for use in steam condensers and other high-temperature environments.
Aerospace Components: The aerospace industry demands materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stresses. CCPs are used in components such as heat shields and structural parts, where both thermal conductivity and mechanical strength are crucial.
Heat Sinks and Thermal Management: Due to their excellent thermal conductivity, CCPs are used in heat sinks and other thermal management solutions to dissipate heat efficiently in electronic devices and high-power equipment.
Marine Engineering: In marine applications, such as seawater piping systems and shipbuilding, CCPs provide excellent corrosion resistance in seawater environments, while the substrate offers the necessary structural strength to handle the stresses of marine operations.
What Are the Limitations of Copper Clad Plates in High-Temperature Applications?
While CCPs offer numerous advantages, there are certain limitations to consider:
Thermal Expansion Mismatch: Differences in the coefficients of thermal expansion between copper and the substrate can lead to thermal stresses during temperature fluctuations, potentially causing delamination or deformation over time.
Cost Considerations: The manufacturing processes for CCPs, such as explosive welding or DBC, can be complex and costly, which may limit their use in cost-sensitive applications.
Material Compatibility: Not all substrate materials are compatible with copper, especially at high temperatures. Selecting appropriate material combinations is crucial to ensure performance and longevity.
How Do Copper Clad Laminates Differ from Copper Clad Plates in High-Temperature Applications?
It's important to distinguish between copper clad plates and copper clad laminates (CCLs), as they serve different purposes and have varying performance characteristics in high-temperature applications:
Copper Clad Laminates (CCLs): These are typically used in the fabrication of printed circuit boards (PCBs). They consist of a resin-impregnated substrate, such as fiberglass or paper, with copper foil bonded to one or both sides. CCLs are designed for electrical insulation and signal transmission rather than structural applications. Their performance at high temperatures depends on the resin system used; for instance, polyimide-based CCLs offer better high-temperature resistance compared to epoxy-based ones.
Copper Clad Plates (CCPs): As discussed, CCPs are composite materials combining copper with a metal substrate like steel or aluminum, providing both structural strength and excellent thermal conductivity. They are suitable for high-temperature structural applications, such as heat exchangers and power electronics substrates.
YOU MAY LIKE












(1)_副本_1734936765500.webp)

(1)_副本_1734935519643.webp)

